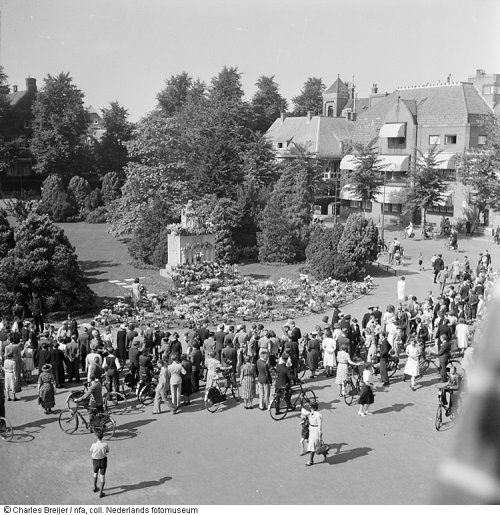Members of the Sadler’s Wells Ballet Company leave Victoria Station, London, for a tour of Holland, May 1940. Director Ninette de Valois is on the far right.
When the Germans invaded Holland on May 10, 1940, Ninette de Valois found herself trapped in The Hague. She was the director of the Sadler’s Wells Ballet Company from England. She and her 42 dancers had been on a Dutch tour. On the day of the invasion, de Valois had been sitting at a sidewalk café with two members of the dance company. It was noon. Suddenly, a stray bullet ricocheted from the pavement, passed between their heads, and crashed through the café’s plate glass window behind them. The bullet had been fired from a German plane swooping over the city square. The diners were rushed inside to safety.
That morning, some of the dancers had flocked to the rooftop of their hotel to watch German parachutists float down and land in the area around the Hague, where Queen Wilhelmina resided. Thousands of leaflets also fluttered down from the enemy aircraft, some landing on the rooftop, that proclaimed:
Strong German troop units have surrounded the city. Resistance is of no use. Germany does not fight your country but Great Britain. In order to continue this battle the German Army has been forced to penetrate your country. The German Army protects the life and goods of every peace-loving citizen. However, the German troops will punish every deed of violence committed by the population with a death sentence.” 1
For five days, the Dutch army fought bravely, but it was no match for the German war machine. The Netherlands had a policy of neutrality and had had no recent experience of resisting outside invading forces. Queen Wilhelmina and the Dutch Royal Family from the Royal House of Orange-Nassau refused to accept the Nazi offer of protection and sailed to England on the HMS Hereford sent by King George VI.

The Exiled Royals with the King and Queen of England, WWII (photo undated). From left to right: Queen Marie of Yugoslavia,Miss Benesj,Queen Wilhelmina of the Netherlands,Miss Raczkiewicz,King George VI of England,King Peter of Yugoslavia,King Haakon of Norway, Queen Elizabeth (The Queen mother) of England, the President of Poland, M. Raczkiewicz and Dr. Benesj, President of Tsjecho- Slovakia.
The Netherlands surrendered on May 15.
For the next seven weeks, the citizens of Holland did not resist the German occupation. They buried their dead and mourned their losses. They were shocked and demoralized. They felt abandoned by their queen.
Audrey Hepburn was eleven years old when the Germans took over her town of Arnhem, Holland:
“The first few months we didn’t quite know what had happened.”
But Queen Wilhelmina reached out to her subjects across the North Sea via newsreels and BBC radio broadcasts, revitalizing Dutch hope for Allied liberation, and condemning German aggression. She urged them to resist the moffen (German Huns). For the next five years, the radio voice of the Queen would be the main source of inspiration for the Dutch Resistance Movement.

Princess Juliana and Prince Bernhard celebrate their engagement 1936. Note the white carnation in the Prince’s lapel.
An opportunity for the Dutch citizens to protest the German occupation arrived on June 29. It was the birthday of Prince Bernhard, the Queen’s son-in-law. Since he had been a student, the Prince had worn a trademark white carnation in his lapel.
So, on June 29, the Dutch people demonstrated their loyalty to Queen and country and their defiance of Nazi rule. People participated all across the country, but the activity was strongest in Amsterdam and The Hague.
People displayed vases full of carnations in the windows of homes and stores. Women and girls wore orange skirts, orange being the national color, symbolic of the Royal House of Orange. The Dutch flag was flown. Men pinned white carnations in the buttonhole of their coats, in imitation of Prince Bernhard, a German who was anti-Nazi. Some people rode bicycles around town all dressed in orange.
Crowds gathered at the statue of Queen Emma, Wilhelmina’s mother, in Amsterdam to lay flowers.
At first, only single flowers were placed on the statue’s lap. Then others arrived carrying great pots of flowers. Soon the area at the base of the statue was covered in flowers. On the nearby lawn, the letter B was formed with a clever flower arrangement. People brought cut-out pictures of the royal family and laid these beside the flowers.
A street organ began to play the national anthem. Softly at first, people began to sing. Shortly, though, more people lifted their voices in patriotic song. Emotion was running high.
Men belonging to the WA, the military arm of the Dutch Nazi organization (NSB), shoved into crowds and started fights. The WA goons wore black shirts. Many people were injured.

NSB members (Dutch Nazis or collaborators) show up at a statue of Queen Emma on Carnation Day, giving the straight arm salute.
People gathered at the Queen’s residence in the Hague, the Noordeinde Palace, to lay flowers on the balcony and to sign the birthday register. The German commander of the Wehrmacht feared a riot. He ordered German fighter planes to fly above the city, diving now and then, but not to shoot, to get the crowd to disperse.
This day became known as Anjerdag, “Carnation Day.”

German propaganda minister Joseph Goebbels (center) is shown at the entrance to Queen Wilhelmina’s residence, the Noordeinde Palace, in The Hague on Carnation Day. The nonviolent protest demonstrations by the Dutch citizens greatly alarmed their German occupiers. Hitler was informed and the Nazis began their crackdown on Dutch life, liberty, and the pursuit of happiness.
The Germans were furious with this civil act of disobedience. They ordered images of the Dutch Royal Family to be removed from all public places. Street names were renamed. The Prince Bernhard Square, for example, became “Gooiplein.” The Royal Library was soon referred to as the National Library. On the first of August, the top Nazi in Holland, Reichskommissar Seyss-Inquart, announced that it was forbidden to celebrate a birthday of a member of the Dutch Royal family.
Postnote: In early 1941, a baby girl was born to a Mr. and Mrs. Niehot of The Hague. They wanted to name their newborn baby Nelia after their midwife, Nelia Epker, but she suggested they give their child an ‘Orange‘ name. The result was announced in the newspaper in a birth advertisement: Irene Beatrix Juliana Wilhelmina Niehot.
This announcement was met with great joy. Irene and Beatrix were the young daughters of Crown Princess Juliana.

May 1940, London. Elizabeth Van Swinderen, wife of the former Dutch minister to Great Britain, points out London barrage balloons to Princess Juliana of the Netherlands, who is pushing the stroller. Juliana is with her children, Beatrix is by her side and Irene is in the baby carriage.
Perfect strangers sent cards, flowers, cakes and even money to the Niehot family. When the midwife Nelia Epker placed a thank-you advertisement in March 1941, listing the baby’s royal names once again, Nelia was arrested. She would not return to the Netherlands until August 1945, a survivor of Camp Ravensbrück. 2
1 Gottlief, Robert, ed. Reading Dance: A Gathering of Memoirs, Reportage, Criticism, Profiles, Interviews, and Some Uncategorizable Extras. New York: Pantheon Books, 2008.