Constance Keane, 19, was sure she had blown her Paramount screen test. It was August of 1941 and the film was “I Wanted Wings.” Keane auditioned to portray a nightclub singer:
“We did a scene in which I was supposed to be tipsy at a table in a small nightclub. Things were going nicely until I leaned my elbows on the edge of the table….My right elbow slipped off the table edge sending my long blonde hair falling over my left eye. I spent the next few minutes trying to continue with the scene as I kept shaking my head to get the hair out of my eyes.” (1)
She knew she had lost the chance to play the part and left the studio sobbing. But then came the phone call from the picture’s director. He wanted her for the part. Her acting may not have been perfect, but she had a magnetism on film and, the biggest surprise of all, her hair had been a smash! He liked the eye-hiding gimmick of it. The picture was going to be a hit, he said, and that would make her Connie a star. A star, however needed both a gimmick and a good name. He hated the name Constance Keane so he rechristened her “Veronica Lake,” borrowing the “Veronica” bit from his secretary and adding the last name “Lake” because “her eyes are calm and blue like a lake.”

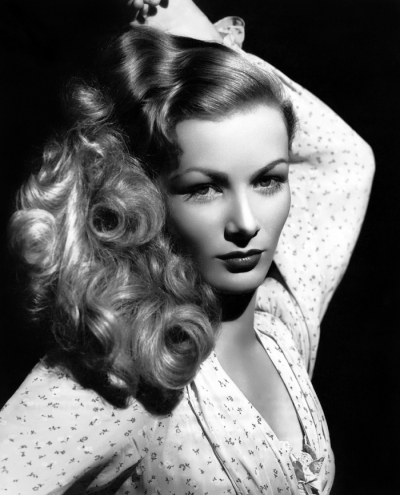
Veronica Lake liked to say that she didn’t do cheesecake shots like Betty Grable but, rather, used her hair for sex appeal. Photo undated, ca. 1942
“I Wanted Wings” was indeed a runaway success. It was the biggest picture of 1941 and Veronica Lake’s breakthrough hit. Veronica Lake (1922-1973) , all 4’11” and 90 lbs of her, became a big star overnight.

To get an idea of how tiny Veronica Lake was, she is shown here with fellow film stars Paulette Goddard (l) and Dorothy Lamour (center). Lake is at our far right. From movie, “Star-Spangled Rhythm,” 1942.
The public loved her playful yet seductive, one-eyed look.

The poster for Paramount’s 1941 film, “I Wanted Wings” launched Veronica Lake’s career and her trademark peekaboo hairdo.
Lake’s honey-blonde hair – flat on top because women wore hats in the forties – was worn with a deep side parting and swept over to the opposite side. Soft waves draped her cheek and a single S-curl fell seductively over one eye. Long and loose, flowing over the shoulders and down the back, the hairstyle known as the “peekaboo” became a fashion must-have.
Women flocked to beauty salons all across the nation to get “The Lake Look.” The Fuller Brush Company advertised that Lake gave her hair fifteen minutes of stroking every day with one of their brushes.
Life magazine devoted an article to her hair and the sensation it caused, divulging such personal information as
“the fact that my head had 150,000 hairs, each measuring about 0.0024 inches in cross-section….[B]ecause Hollywood’s water was so hard, I rinsed [my hair] in vinegar,” wrote Lake. (1)
For the next several years, Lake’s hair would have the tendency to droop over one eye.
Her role in her next picture, “Sullivan’s Travels,” (1942), costarring Joel McCrea, won her both popular and critical acclaim. It was straight comedy and Lake proved to be very good at it.
Her next film, “This Gun for Hire” (1942), a film noir, was the first of seven she made with Alan Ladd. Both Lake and Ladd were short – Ladd was only 5’5″ – golden-haired, attractive, and aloof. The public loved the Ladd/Lake pairing (and Ladd didn’t have to stand in a pit when filming scenes with his leading lady).
In “I Married a Witch” (1942), a romantic fantasy comedy, Lake is cast as a witch whose plans for revenge against costarring mortal Frederic March are foiled. Her characterization is a funky combination of kittenish allure and goofiness. The film was wildly popular and later sparked the creation of the TV series, “Bewitched” in 1964.

On the set of “I Married a Witch,” Veronica Lake made Frederic March miserable because, in real life, she hated him. In one tender scene, the camera is filming Frederic March from the neck up while Lake is kneeing him in the groin. That was not in the script and March kept a poker face despite excruciating pain.

In “I Married A Witch,” Veronica Lake plays a witch burned in the Salem witch trials, out to seek revenge.
In 1943, Veronica Lake was as popular as ever with the movie-going public. She was on a roll. She was one of Hollywood’s most glamorous stars.
Unfortunately, Miss Lake’s rise to fame coincided with America going to war (World War II, 1941-1945). Men left for the battlefield and women went to work in war industry factories.

Women were invaluable in the war effort. Soldiers without Guns poster, Office of War Information, ca. 1944. (National Archives)
Some of these factory workers wore their hair down in the factories, peekaboo style. Their drooping locks began to present a safety issue. The U.S. government intervened, asking the one-eyed beauty Veronica Lake not to wear her hair down for the duration of the war. She obliged, putting her hair up, and was praised widely for her patriotism, giving up her peekaboo look for the war effort.

In this Life magazine photo, movie star Veronica Lake illustrates the danger of loose hair for female factory workers. Her hair is tangled in machinery. Photo Undated. Ca. 1943
Here is the public service announcement, “Safety Styles” she made to urge women to follow her example:
At the end of the “Safety Styles” video, the announcer says that, with her new updo, Veronica Lake’s “hair is out of the way and combed in a simple and becoming fashion.” That fashion was called a “victory roll,” making a “V” shape when seen from the back and a “victory” because of the gesture of choosing country over vanity. In the 1943 film, “So Proudly We Hail!” (1943), Lake wears her hair in a “victory roll” in her portrayal of Lieutenant Olivia D’Arcy. The movie was a success.
In 1944, Lake’s career faltered with her unsympathetic role as Nazi spy Dora Bruckman in “The Hour Before the Dawn” (1944). The movie was a flop. Again, Lake is wearing her hair up in a severe style, as the war is still in progress.
Veronica Lake would make 26 pictures. By 1950, however, her career in films was effectively over. Some biographers say that abandoning her classic peekaboo hairstyle damaged her box office appeal. In truth, though, it was Lake’s heavy drinking and her devilish behavior that undid her hard-earned success. From the beginning, she was difficult to work with; she made enemies on every movie set, often running off and disappearing in the middle of filming. No one wanted to work with her. The studio stopped giving her plum roles.
Eddie Bracken, her co-star in “Star Spangled Rhythm” (in which Lake appeared in a musical number) was quoted as saying,
“She was known as ‘The B—h’ and she deserved the title.”
Joel McCrea, her co-star in “Sullivan’s Travels,” reportedly turned down the co-starring role in “I Married a Witch,” saying,
“Life’s too short for two films with Veronica Lake.”
(However, McCrea did co-star with Lake again in 1947 in the western, “Ramrod.”)
During filming of the film “The Blue Dahlia” (1946), screenwriter Raymond Chandler referred to her as “Moronica Lake”.
Lake’s romantic entanglements were a disaster. She grew tired of her children. Her mother claimed that Veronica had been diagnosed with schizophrenia as a teen and that she took her to Hollywood to study acting as therapy. Few people trust her mother’s words since she later sued Veronica Lake, wanting part of her estate. Nevertheless, Veronica Lake had a complex and volatile nature.
By 1948, her movies had become flops. Paramount Pictures did not renew her contract.
Veronica Lake’s decline in mental health and descent into full-blown alcoholism was both severe and dramatically rapid. Her beauty faded; her health crumbled. In 1973, after years of ill health, menial jobs largely in hotels and bars, loneliness, numerous brushes with the law for public intoxication and disorderly conduct, and poverty due to untreated alcoholism, Veronica Lake, 51, died of cirrhosis of the liver and hepatitis in a Vermont hospital.
Veronica Lake’s iconic look is still copied today. Countless Youtube tutorials teach how to achieve the peekaboo look, a classic style, a relic of the Golden Age of Hollywood, when Veronica Lake reigned.
Source:
(1) Lake, Veronica with Bain, Donald. Veronica. New York: The Citadel Press, 1969.




































































 “Watch on the Rhine,” with Bette Davis and Paul Lucas, and “OSS,” with Alan Ladd. All of those are great movies.
“Watch on the Rhine,” with Bette Davis and Paul Lucas, and “OSS,” with Alan Ladd. All of those are great movies.


















